
Many of us are aware of Bloom’s Taxonomy in regards to K-12 classrooms, but not in the business setting. To succeed in business training, the trainer must understand the different levels of learning required for a business objective. Whenever new training is required, you must build a solid foundation at the base level of Bloom’s Taxonomy before going to the next level. This article tells you how to use Bloom’s Taxonomy in business learning.
Objectives Made Easier

Bloom’s Taxonomy, as you may already know, is a standardized categorization of learning objectives in an educational context. Bloom’s Taxonomy was created by Benjamin Bloom during the 1950s and it can help you to identify and develop objectives and specify exactly what the learner should be able to do when the training is over. When applied to eLearning solutions, categorizing the levels of reasoning skills required in business can be made easier with Bloom’s Taxonomy.
Bloom’s Taxonomy Levels
As per Bloom’s Taxonomy, there are six levels as we move from the lowest order to the highest. Different forms of learning could occur on every single level and they can include,
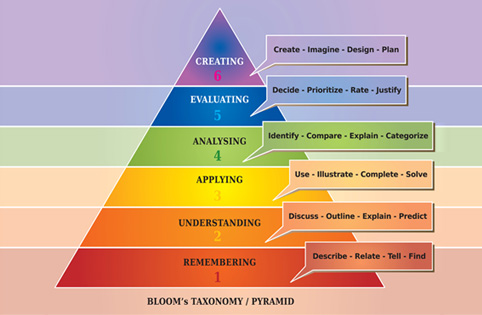
Remembering:
Though there is just rote memorization and recollection of facts without much understanding, this level could be considered a pillar of the learning model because this level acts as a catalyst to unlock the next levels. For example, the necessary information could be in a job aid and where you can source that particular job aid.
Understanding:
At this level, one began to understand. At this level, you can compare, interpret and give descriptions of what you have learned. Understanding a concept can be a game-changer in the successful learning of any learner. For example, it could be to understand the new contract language and how it applies to your job.
Applying
At this level, the learner would apply his knowledge in real life. This level requires a slightly deeper grasp of concepts so you can apply a particular method to solve a problem. For example, it could be to utilize a new tool to make a sale to a customer.
Analyzing
Analyzing is an imperative task and at this level, the learner must be able to assess the main features of any number of new products and contrast the benefits of your organization.
Evaluating
Evaluating is a skill level that enables learners to judge based on strong reasoning. Example: It could be to evaluate a new feature of a tool or system.
Creating
At this level, the learner must be able to create something out of the training-learning process. For example, it could be how to use the latest software to design a new product.
Building a solid foundation for Business Learning

In an organization, as someone moves up to the levels, learning becomes more complex and needs to be supported by an eLearning course or subsequent follow-up sessions or job aids. More time, practice, and support are required, when the thinking and connections that need to occur become more complex. The learners in a business setting are adults. We must know what level of reasoning skills are required to meet the learning objective when creating eLearning solutions for adult learners. Before climbing to the next level of learning, we must make sure that the learner built a strong foundation at the current level. To measure the kind of learning, Bloom’s Taxonomy is a great advantage.
Final Notes

Word choice can make a big difference to your audience. Isn’t it an added advantage to translate your verbs into actionable activities for your learners? Blooms taxonomy model helps us to understand why we should start from the base level and not from the middle of the learning pyramid, thereby adding true value for the learners in the business setting.












